The link between social media and mental health has become one of the most talked-about topics in today’s digital world. As social media platforms continue to grow and evolve, their impact on mental health—both positive and negative—has become impossible to ignore.
While some social media apps offer valuable spaces for emotional support and community, others contribute to poor mental health, especially among young adults and in youth mental health. From helpful connections to increasing mental health concerns like anxiety and depression, the effects of social media usage are complex.
Studies have also found that excessive time spent online can worsen mental health problems and exacerbate existing mental health issues. In this article, we’ll explore both the positives and potential harms of social media, discussing how social media affects emotional well-being, the risks of social media addiction, how screen time influences daily life, and strategies for building healthier online habits.
If You Are a Provider Needing a Marketing Partner Check Some of Our Services:
The Complex Relationship Between Social Media and Mental Health
The interplay between social media and mental health is multifaceted, encompassing both beneficial and detrimental effects. On one hand, social media platforms offer avenues for connection, self-expression, and access to supportive communities. On the other, excessive or negative interactions can contribute to mental health challenges.
A 2022 Pew Research Center study revealed that 35% of U.S. teens report using at least one social media platform “almost constantly.” Notably, 54% of teens indicated that it would be hard to give up social media, underscoring its integral role in their daily lives.
The impact of social media varies among different age groups. Young people, particularly adolescents, may be more susceptible to the negative effects due to developmental factors and social pressures. Conversely, young adults might leverage social media for networking and professional growth, though they are not immune to its adverse effects.
Understanding this complex relationship is crucial for developing strategies that maximize the positive aspects of social media while mitigating its potential harms.
Teen Social Media Usage Patterns (2023)
| Platform | Almost Constantly | Several Times a Day | About Once a Day | Several Times a Week | Less Often | Do Not Use | NET Daily Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YouTube | 16% | 38% | 17% | 15% | 7% | 7% | 71% |
| TikTok | 17% | 32% | 9% | 10% | 7% | 25% | 58% |
| Snapchat | 14% | 29% | 8% | 11% | 7% | 31% | 51% |
| 8% | 27% | 12% | 13% | 8% | 32% | 47% | |
| 3% | 8% | 8% | 8% | 9% | 63% | 19% |
Positive Effects of Social Media on Well Being
When used intentionally, social media can provide powerful benefits for mental health. Many young adults and young people use social platforms to find emotional support during difficult times. In fact, many teens report that social media has helped them feel more connected to others who share similar struggles, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Through online social interactions, individuals can engage in self expression by sharing their stories, interests, and achievements. This connection to broader communities can be especially meaningful for those facing mental health challenges such as anxiety or depression. By encouraging people to seek support and offering a place to belong, social media platforms can become lifelines for social media users who feel misunderstood in their everyday life.
Many organizations and advocates also use+ social media to raise awareness about important mental health topics, helping others recognize signs of distress and normalizing conversations about emotional struggles. This empowers human beings to take charge of their own lives and support one another.
Practicing healthy social media use means setting appropriate boundaries, focusing on uplifting communities, and using tools like parental control apps to monitor social media use, especially among younger audiences. Building a healthy relationship with social media allows individuals to enjoy its benefits without overwhelming their mental health. By using social media mindfully, people can foster positivity, connection, and personal growth in their daily lives.

Negative Effects of Social Media on Mental Health

Despite its potential for connection, social media can also contribute to serious mental health challenges. A growing body of research shows that frequent social media use is linked to low self esteem, depressive symptoms, and psychological distress, particularly among younger social media users. The negative effects of digital interactions can erode emotional resilience and worsen overall well being.
Excessive social media use can amplify these risks. A Clinical Psychological Science study found an increased risk of depression among teens who reported over three hours of screen time daily. The constant comparison, fear of missing out, and pressure to curate a perfect image can trigger anxiety, fuel mood disorders, and disrupt mental health stability. Excessive media screen time has also been tied to sleep problems, which further diminish mental wellbeing.
Behavioral patterns like the need to constantly check social media stem from disruptions in the brain’s reward center, where dopamine-driven behaviors impair impulse control. This cycle fosters addiction to social media, increasing emotional vulnerability over time.
Negative social media affects extend beyond self-perception. Exposure to online abuse, spreading hurtful rumors, and hostile interactions can leave lasting emotional scars. Studies published in the International Journal of Mental Health Systems highlight that such experiences have a negative impact on emotional development, especially among younger users who frequently access social media across many platforms.
Social isolation is another hidden danger. Instead of deepening real-world relationships, excessive virtual engagement can cause users to feel more disconnected, leading to mental illness symptoms and even suicide related outcomes in extreme cases.
Maintaining balance between digital life and physical activity is crucial to preserving both emotional and physical well being. Understanding these effects equips individuals to approach social media with greater awareness and healthier habits.
Social Media Addiction and Its Impact on Mental Health
Social media addiction is a behavioral dependency where individuals feel a compulsion to engage with social media apps, often at the expense of their mental and emotional health. Unlike casual use, addiction disrupts daily routines, relationships, and even self-care, creating a loop that’s difficult to escape.
At the core of this behavior is the brain’s reward center. When users receive likes, messages, or follows, it activates dopamine responses—temporary bursts of pleasure that condition the brain to seek more. Over time, this reinforcement loop can impair impulse control, especially in teens and young adults whose prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for decision-making and self-regulation, is still developing.
People struggling with this addiction may constantly check social media without realizing it, even in inappropriate or dangerous contexts like while driving or in the middle of social interactions. This unchecked behavior isn’t just a bad habit—it’s a potential red flag for deeper mental health issues.
Research links compulsive use to heightened anxiety, attention problems, and even mental illness. As boundaries between real life and digital life blur, those addicted to social media apps often experience greater emotional volatility, social withdrawal, and increased sensitivity to online feedback.
Without intervention, social media addiction can exacerbate pre-existing conditions or serve as a gateway to new mental health struggles. Recognizing the signs early—and understanding the neurological factors behind them—is a critical first step in reducing harm and promoting recovery.
Screen Time, Social Media Use, and Mental Health Concerns
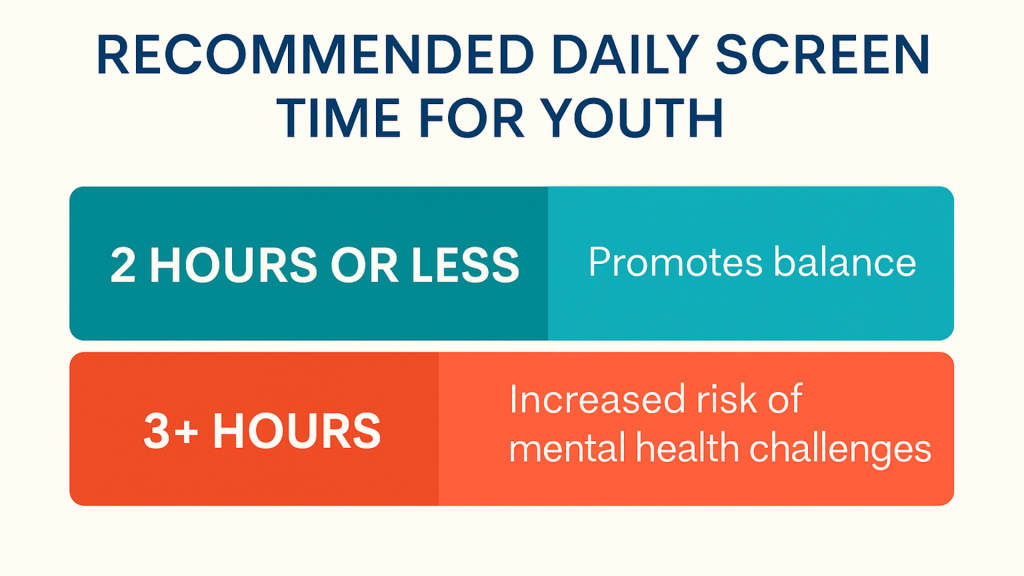
The growing presence of screen time, media screen time, and social media usage has created new challenges for youth mental health. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, excessive screen time—especially beyond three hours per day—has been associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances among adolescents.
Social media use adds another layer to this concern. Constant connectivity exposes young social media users to an overwhelming amount of content that can disrupt emotional regulation and contribute to emotional fatigue. Tools like parental control apps are becoming essential, offering families a way to set healthy digital limits and safeguard mental wellbeing.
A systematic review of studies found that structured media use habits—not complete avoidance—are most effective in supporting positive development. Managing social media exposure during key developmental stages helps prevent emotional overwhelm and promotes healthier cognitive patterns. Awareness of these habits is crucial, especially in light of the Surgeon General’s Advisory calling for stronger protections around children’s digital experiences.
How Social Media Platforms Influence Everyday Life
Many social media platforms have seamlessly woven themselves into the fabric of life and heavily influence how people perceive their own lives. While offering avenues for connection and entertainment, social platforms also foster constant comparison—a phenomenon that the Pew Research Center identifies as a significant contributor to body image issues, envy, and emotional fatigue.
When individuals measure their success, happiness, or attractiveness against curated images online, it can create negative experiences that diminish authentic self-esteem. For social media users, this distortion of reality is rarely conscious but steadily erodes emotional security over time. Recognizing the difference between online portrayals and real life is an essential skill in today’s digital world.
Potential Harms of Social Media for Young Adults
For young adults, the harms of social media use often stem from relational conflicts and reputational damage. Platforms amplify risks like spreading hurtful rumors, where even a single post can leave lasting emotional scars. This rapid amplification of negativity is deeply concerning for mental health professionals.
Studies show that the anonymity and speed of online interactions lower empathy among social media users, leading to harsher judgments and impulsive, damaging comments. These experiences can directly undermine mental resilience, leading to elevated anxiety, depression, and distrust in real-world relationships. As young people build their identities, such negative impact during vulnerable years can have lasting psychological consequences.
Building a Healthy Relationship with Social Media
Developing a healthy relationship with social media begins by establishing appropriate boundaries. Strategies such as scheduling daily “offline hours,” turning off non-essential notifications, and engaging in daily physical activity provide essential counterbalances to virtual life.
Maintaining digital balance also means monitoring emotional reactions during social media use. If a platform consistently causes anxiety, irritability, or self-criticism, it may signal a need for a break or a shift in focus toward more uplifting communities. Replacing some social media use with meaningful offline activities strengthens real-world connections and restores mental energy.
Practical steps—like keeping phones outside the bedroom at night and prioritizing face-to-face conversations—create healthier habits without needing to abandon technology altogether. Healthy digital engagement enhances wellbeing instead of undermining it.
Seeking Support for Mental Health Issues in a Digital Age
When mental health concerns arise from social media use, reaching out for help is vital. Many people suffering online isolation or emotional distress hesitate to seek help due to stigma or uncertainty.
However, social media itself offers spaces for emotional support, from therapy-focused forums to recovery groups. Recognizing when digital life is negatively affecting emotional health—and taking proactive steps to find assistance—can prevent long-term damage.
Whether through professional counseling, peer support groups, or family interventions, healthy social media use means knowing when to unplug and connect with real-world solutions.

